

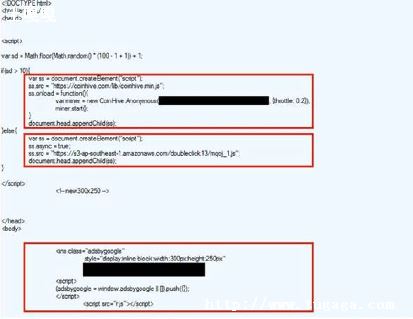
返回结果 将返回结果放到spark rdd 例如: JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
如果你的项目是java项目的话,就需要使用hive提供的java api,如下代码:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
/**
* Hive的JavaApi
*
* @author 吖大哥
*/
public class HiveJdbcCli {
private static String driverName = "org.apache.hadoop.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver";
private static String user = "hive";
private static String password = "mysql";
private static String sql = "";
private static ResultSet res;
private static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(HiveJdbcCli.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
conn = getConn();
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 第一步:存在就先删除
String tableName = dropTable(stmt);
// 第二步:不存在就创建
createTable(stmt, tableName);
// 第三步:查看创建的表
showTables(stmt, tableName);
// 执行describe table操作
describeTables(stmt, tableName);
// 执行load data into table操作
loadData(stmt, tableName);
// 执行 select * query 操作
selectData(stmt, tableName);
// 执行 regular hive query 统计操作
countData(stmt, tableName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.error(driverName + " not found!", e);
System.exit(1);
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.error("Connection error!", e);
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
conn = null;
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
stmt = null;
private static void countData(Statement stmt, String tableName)
throws SQLException {
sql = "select count(1) from " + tableName;
System.out.println("Running:" + sql);
res = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
System.out.println("执行"regular hive query"运行结果:");
while (res.next()) {
System.out.println("count ------" + res.getString(1));
private static void selectData(Statement stmt, String tableName)
sql = "select * from " + tableName;
System.out.println("执行 select * query 运行结果:");
private static void loadData(Statement stmt, String tableName)
String filepath = "/home/hadoop01/data";
sql = "load data local inpath '" + filepath + "' into table "
+ tableName;
private static void describeTables(Statement stmt, String tableName)
sql = "describe " + tableName;
System.out.println("执行 describe table 运行结果:");
private static void showTables(Statement stmt, String tableName)
sql = "show tables '" + tableName + "'";
System.out.println("执行 show tables 运行结果:");
if (res.next()) {
System.out.println(res.getString(1));
private static void createTable(Statement stmt, String tableName)
sql = "create table "
+ tableName
+ " (key int, value string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'";
stmt.executeQuery(sql);
private static String dropTable(Statement stmt) throws SQLException {
// 创建的表名
String tableName = "testHive";
sql = "drop table " + tableName;
return tableName;
private static Connection getConn() throws ClassNotFoundException,
SQLException {
Class.forName(driverName);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return conn;
String sql="show tables; select * from test_tb limit 10";
ListString command = new ArrayListString();
command.add("hive");
command.add("-e");
command.add(sql);
ListString results = new ArrayListString();
ProcessBuilder hiveProcessBuilder = new ProcessBuilder(command);
hiveProcess = hiveProcessBuilder.start();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
hiveProcess.getInputStream()));
String data = null;
while ((data = br.readLine()) != null) {
results.add(data);
其中command可以是其它Hive命令,不一定是HiveQL.
以上参数下面有详解.
LogTest.java代码如下
* @author Administrator
public class LogTest {
* 采用单例模式
static Logger logger = null;
public static void testAddMethod(EmployeeDao empDao,Employee emp) throws ClassNotFoundException{
logger=Logger.getLogger(EmployeeDao.class.getName());
logger.info("Info "+EmployeeDao.class.getName()+"\t "+" \t param="+emp.getClass().getName());
//获取类的相应方法
logger.warn("Warn ...");
logger.error("Error ...");
EmployeeDao.java文件代码如下:
public class EmployeeDao {
public void addEmployee(Employee emp){
System.out.println(emp.getEmpId()+" "+emp.getEmpName());
Employee.java代码如下:
public class Employee {
private int empId;
private String empName;
public int getEmpId() {
return empId;
public void setEmpId(int empId) {
this.empId = empId;
public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
EmployeeJuint.java代码如下:
import org.junit.Test;
* @author tfq
public class EmployeeJuint {
@Test
public void addEmployee(){
Employee emp=new Employee();
emp.setEmpId(1);
emp.setEmpName("tfq");
EmployeeDao empDao=new EmployeeDao();
//打印日志
//LogTest.testAddMethod(EmployeeDao.class.getName());
//LogTest.testAddMethod(empDao);
LogTest.testAddMethod(empDao,emp);
empDao.addEmployee(emp);
①.、定义配置文件
①配置根Logger,其语法为:0
②配置日志信息输出目的地Appender,其语法为:
...
③配置日志信息的格式(布局),其语法为:
%p 输出优先级,即DEBUG,INFO,WARN,ERROR,FATAL
%c 输出所属的类目,通常就是所在类的全名
%t 输出产生该日志事件的线程名
%n 输出一个回车换行符,Windows平台为"\r\n",Unix平台为"\n"
①得到记录器
public static Logger getLogger( String name)
通过指定的名字获得记录器,如果必要的话,则为这个名字创建一个新的记录器.Name一般取本类的名字,比如:
②读取配置文件
PropertyConfigurator.configure ( String configFilename) :读取使用Java的特性文件编写的配置文件.
DOMConfigurator.configure ( String filename ) :读取XML形式的配置文件.
③插入记录信息(格式化日志信息)
当上两个必要步骤执行完毕,就可轻松地使用不同优先级别的日志记录语句插入到您想记录日志的任何地方,其语法如下:
Logger.debug ( Object message ) ;
Logger.info ( Object message ) ;
Logger.warn ( Object message ) ;
Logger.error ( Object message ) ;
//得到当前jsp路径
String prefix = getServletContext().getRealPath("/");
Class.forName("org.apache.hadoop.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver");
String selectSql = "select * from db.data where address = '11111111'";
PreparedStatement state = null;
state = connect.prepareStatement(selectSql);
ResultSet resultSet = state.executeQuery();
while (resultSet != null resultSet.next()) {
} catch (Exception e) {